The U.S. added 15 GW of power generation in the first half of 2022, according to a survey report released by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). The top three power generation technologies are wind power generation facilities (5.2GW), natural gas power generation facilities (4.3GW), and photovoltaic systems (4.2GW), followed by battery energy storage systems.
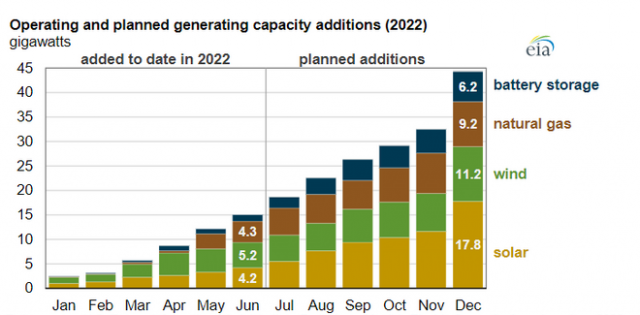
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), the PV systems installed will account for the largest share of new capacity additions by the end of the year, reaching 17.8GW; followed by wind (11.2GW), natural gas (9.2GW), battery storage energy system (6.2GW). That means energy developers will add 29GW of power generation to the grid in the second half of this year.
More than 40% of the wind power facilities opened in the United States this year are deployed in Texas, of which 2.2GW of wind power facilities have been connected to the grid. Some of the largest wind projects installed and commissioned this year include the 999MW Traverse wind project in Oklahoma, the 492MW Maverick Creek wind project in Texas, and the 440MW photovoltaic system and The Slate Hybrid project for battery energy storage systems.
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) also tracks operational projects with an installed capacity of more than 1MW. Nationally, there are already 497 gas-fired power plants, 202 coal-fired power plants, 138 wind power facilities, 95 nuclear power plants, 80 conventional hydropower plants, and 66 utility-scale photovoltaic power plants, the survey showed. Those numbers are expected to change as new renewable power generation projects come online and coal, natural gas, and nuclear power plants are decommissioned.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), 15.1GW of conventional power generation facilities are expected to be phased out this year, while about 8.8GW of conventional power generation facilities have been closed or eliminated so far this year. Coal-fired power plants will account for the largest share of decommissioned generation facilities due to their high carbon emissions and will account for about 76% of all decommissioned generation facilities. This is followed by natural gas (12%) and nuclear power plants (9%). For example, a 1.3GW coal-fired power plant in Ohio was retired in May, and a 1.2GW-fired power plant in Maryland was retired in June. In addition, a 769MW nuclear power plant in Michigan was decommissioned in June this year.


